CSV files have become the backbone of data exchange in modern business operations. Understanding what is a CSV file and how to work with data using this widely used format can streamline your workflows and prevent costly errors.
Key takeaways
- CSV files are plain text documents that store data using comma-separated values, making them universally compatible with spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets
- The CSV file format excels at data exchange between different applications due to its simple structure and broad software support
- The correct format for a CSV file depends on consistent delimiters, UTF-8 encoding, and standardized data entry practices
- CSV files are used for data migration, contact management, e-commerce catalogs, and business reporting across industries
- While CSV files offer simplicity advantages, they have limitations with complex data structures compared to formats like JSON or XML
Understanding What is a CSV File Format
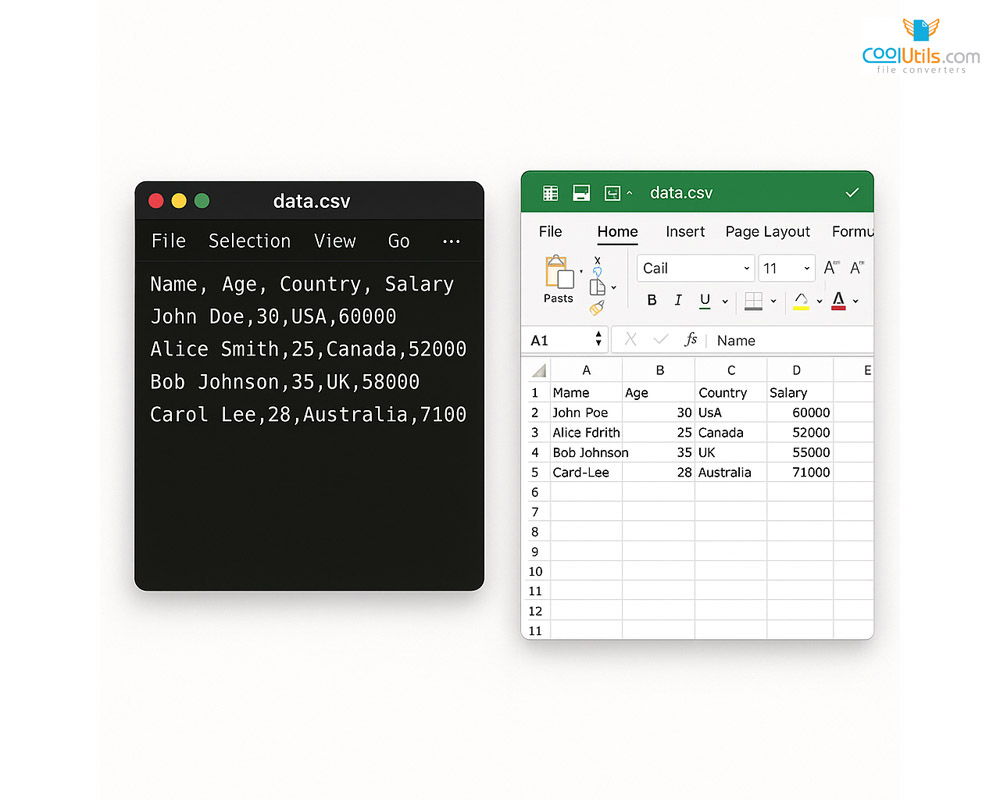
What is a CSV file? A CSV file is a plain text file that stores data in a tabular format using comma-separated values. The CSV file format represents one of the most common file formats for storing and transferring data between different software applications. CSV files are compatible with virtually every system and can be opened as plain text files where each line represents a data record, and commas separate individual fields.
Key characteristics of CSV files include:
- Plain text format readable by any text editor
- Uses commas as default delimiters to separate data fields
- Each row represents a complete data record
- First row typically contains column headers
- Compatible with Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and other spreadsheet programs
- Compact file sizes compared to other structured formats
What Does CSV Stand For?
CSV stands for “Comma-Separated Values,” which directly describes how the format organizes data. In a CSV file, commas act as delimiters that separate individual data fields, while line breaks separate complete records.
The Anatomy of a CSV File
Understanding CSV file structure requires examining its core components: headers, records, fields, and delimiters. Headers appear in the first row and contain column names. Records represent individual entries, with each record occupying its own line.
CSV File Delimiters
While commas serve as the standard delimiter, CSV files can use alternative separator characters depending on regional preferences.
| Delimiter Type | Character | Usage | Example |
| Comma | , | Standard CSV format | name,age,city |
| Semicolon | ; | European formats | name;age;city |
| Tab | \t | Tab-separated values | name age city |
| Pipe | | | Database exports | name|age|city |
What is the Correct Format for a CSV File?
The correct format for a CSV file follows established conventions that ensure compatibility across different systems. While RFC 4180 provides guidelines, most applications implement variations based on specific requirements.
CSV format comparison across regions:
| Format Type | Delimiter | Decimal | Date Format | Example |
| US Standard | Comma | Period | MM/DD/YYYY | John,25,12.50,01/15/2024 |
| European | Semicolon | Comma | DD.MM.YYYY | John;25;12,50;15.01.2024 |
| International | Comma | Period | YYYY-MM-DD | John,25,12.50,2024-01-15 |
What is a CSV File Used For? Common Applications
CSV files serve diverse purposes across industries due to their simplicity and universal compatibility. Understanding what a CSV file is used for helps organizations leverage this format for efficient data management.
CSV file applications by industry:
- E-commerce: Product catalogs, inventory updates, order processing
- Marketing: Customer lists, email campaigns, lead tracking
- Finance: Transaction records, account data, financial reporting
- Healthcare: Patient records, medical data exchange
- Education: Student information, grades, enrollment data
Data Exchange and Integration
CSV files excel at facilitating the ability to transfer data between different systems and software applications. When direct database connections aren’t feasible, CSV format serves as a reliable intermediate format for system integration projects.
System integration workflow:
- Export data from source system to CSV format
- Validate data structure and field mapping
- Transform data to match target system requirements
- Import CSV data into destination system
- Verify successful data transfer and integrity
Data Analysis and Reporting
Data analysts rely on CSV files for importing raw data into analytical tools and spreadsheet software. The format’s compatibility with tools like Excel, Python, and R makes it ideal for data processing workflows.
E-commerce and Shopping Cart Migration
E-commerce platforms extensively use CSV files for managing product catalogs and facilitating platform migrations. Major platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento support CSV-based imports for products, customers, and orders.
Creating and Editing CSV Files
Creating CSV files and learning how to create a CSV file can be accomplished through various methods, from simple text editors to sophisticated spreadsheet applications.
What is a CSV File in Excel: Working with Spreadsheets
Microsoft Excel provides the most user-friendly approach for creating and learning how to edit a csv file. Understanding what is a CSV file in Excel helps users leverage familiar spreadsheet functionality.
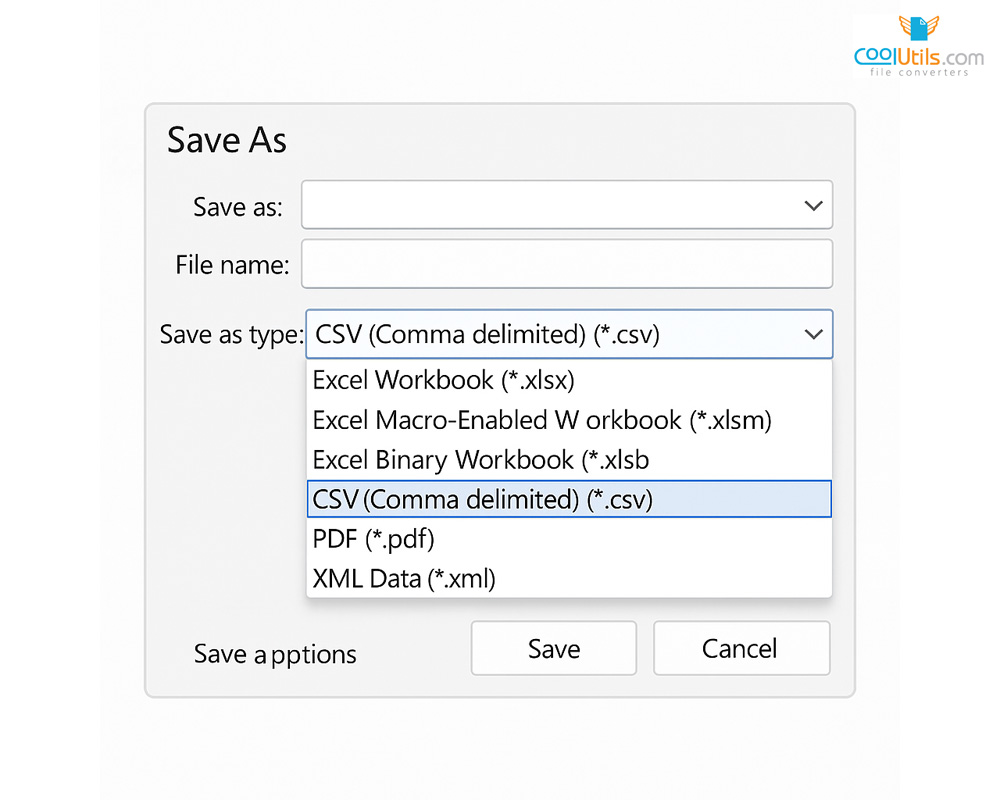
Steps for creating CSV files in Excel:
- Open Microsoft Excel and create a new workbook
- Create the headings in the first row for your data columns
- Add data in subsequent rows with consistent field structure
- Select “File” > “Save As” from the menu to save a new file
- Choose “CSV (Comma delimited)” from format options
- Click “Save” and accept any feature compatibility warnings
Using Text Editors and Programming Languages
Text editors offer direct control over creating a csv file and are particularly useful for quick edits or when working with large datasets. Programming languages like Python provide powerful libraries for CSV manipulation through tools like Pandas.
CSV Command Line Tools
Specialized command-line tools like xsv and csvkit provide efficient solutions for processing large CSV files that exceed the capabilities of traditional desktop applications.
Importing and Exporting CSV Data
Successfully importing and exporting CSV data requires understanding platform-specific requirements, validation procedures, and common troubleshooting techniques.
Database Imports and Exports
Database management systems provide built-in functionality for CSV operations. MySQL’s LOAD DATA INFILE command, PostgreSQL’s COPY function, and SQL Server’s bulk insert capabilities offer efficient methods for transferring large datasets.
CRM and Marketing Platform Integration
Customer relationship management systems heavily depend on CSV imports for contact list management. Platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Mailchimp provide detailed field mapping tools to ensure successful imports.
Best practices for CRM CSV preparation:
- Validate email addresses using proper format standards
- Standardize phone number formats across all records
- Ensure consistent name capitalization and formatting
- Remove duplicate entries before importing
- Verify all required fields contain valid data
Handling Special Characters and Encoding
Character encoding represents one of the most common challenges in CSV file management. UTF-8 encoding provides optimal compatibility for international characters.
Common special character issues and solutions:
- Commas in data: Enclose fields containing commas in double quotes
- Quotation marks: Escape with double quotation marks
- Line breaks: Replace with spaces or encoded representations
- Formula characters: Prefix with apostrophe to prevent injection attacks
CSV File Advantages and Limitations
Understanding when to use CSV files versus alternative formats requires analyzing their strengths and limitations.
When to Use CSV Files
CSV files excel in scenarios requiring simple tabular data representation and broad software compatibility.
Optimal CSV use cases:
- Simple tabular data with consistent structure
- Cross-platform data exchange requirements
- Small to medium datasets (under 1 million rows)
- Legacy system integration projects
- Educational and training environments
When to Consider Alternatives
Complex data structures requiring hierarchical relationships need more sophisticated formats like JSON, XML, or different file types specific to databases.
Efficiency and Performance Considerations
CSV files offer excellent performance characteristics for read and write operations due to their simple structure. Parsing CSV data requires minimal processing overhead.
Best Practices for CSV File Management
Effective CSV file management requires systematic approaches to data organization, quality control, and error prevention.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Validation
Data validation procedures should verify field formats, check for required values, and identify inconsistencies before importing CSV files.
Essential validation checks:
- Verify proper file extension (.csv)
- Check delimiter consistency throughout file
- Validate header row format and completeness
- Confirm data types match expected formats
- Test with sample data before full import
Security Considerations for CSV Files
CSV files present security risks including injection attacks and data exposure.
CSV security best practices:
- Sanitize input data to prevent formula injection
- Validate all imported content before processing
- Use secure file transfer protocols for sensitive data
- Implement access controls and audit logging
- Train users on CSV security risks and prevention
Version Control and Collaboration
Managing CSV files in collaborative environments requires clear naming conventions, change tracking procedures, and conflict resolution strategies when teams work with spreadsheets.
Troubleshooting Common CSV Issues
CSV file problems typically fall into predictable categories, making systematic troubleshooting approaches highly effective.
Fixing Import and Export Errors
Common import errors include delimiter mismatches, character encoding problems, and field mapping issues.
Common CSV errors and solutions:
| Error Type | Typical Cause | Solution |
| Import failure | Delimiter mismatch | Verify and adjust delimiter settings |
| Corrupted characters | Encoding issues | Convert to UTF-8 encoding |
| Missing data | Empty required fields | Fill fields or set default values |
| Parse errors | Special characters | Properly escape problematic characters |
Dealing with Large CSV Files
Large CSV files exceeding standard application limits require specialized handling techniques. File splitting strategies divide datasets into manageable chunks while maintaining data relationships.
What is a CSV File Extension and Other Technical Details
The CSV file extension (.csv) serves as a standard identifier that enables operating systems and software applications to recognize the format. Files can be opened in Microsoft Excel or other programs once this extension is recognized. Understanding what is a CSV file extension and its technical specifications helps ensure proper implementation.
Technical specifications:
- File extension: .csv
- MIME type: text/csv
- Character encoding: UTF-8 (recommended)
- Specification reference: RFC 4180
Comparing CSV with Other Data Formats
Selecting the appropriate file type requires understanding CSV capabilities compared to alternatives.
CSV vs. JSON
CSV excels at representing flat, tabular data structures, while JSON supports hierarchical, nested data relationships. JSON offers better support for complex data types but CSV remains more accessible to non-technical users.
CSV vs. XML
XML provides more structure and metadata capabilities compared to CSV, making it suitable for document-oriented data and complex schema requirements. CSV offers better performance for straightforward data exchange scenarios.
Conclusion
CSV files remain fundamental tools in modern data management, offering unmatched simplicity and compatibility for tabular data operations. Besides csv files, alternatives like JSON and XML exist, but understanding what is a CSV file, proper formatting requirements, and implementation strategies enables organizations to leverage this versatile format effectively. While CSV files have limitations with complex data structures, their universal accessibility makes them indispensable for data exchange and migration across diverse business environments.
FAQs
What is a CSV file used for?
CSV files store and transfer tabular data between applications, enabling data exchange, analysis, reporting, and migration operations across various software platforms and business systems.
How to convert PDF to CSV file?
Use online conversion tools or specialized software to extract tabular data from PDFs, then export the information in CSV format for further processing and analysis.
How do I convert a File to CSV?
Open the file in appropriate software like Excel or Google Sheets, then use “Save As” or export functions to convert data into CSV format.
Can Acrobat convert PDF to CSV?
Adobe Acrobat can convert PDF tables to Excel format, which can then be saved as CSV. Direct PDF-to-CSV conversion requires specialized conversion tools.
What program creates CSV files?
Any text editor, spreadsheet application, database software, or programming language can create CSV files using proper formatting and delimiter conventions for data organization.
Can I make an Excel File a CSV file?
Yes, use Excel’s “Save As” function and select “CSV (Comma delimited)” format to convert Excel files while preserving data structure and content integrity.
Can I create a CSV file without Excel?
Yes, use text editors, Google Sheets, programming languages, online tools, or other spreadsheet applications to create properly formatted CSV files without requiring Excel.