
Table of Contents
What Is a JPG Format: Complete Guide and Tutorial
In the world of digital photography and web graphics, jpg files are among the most commonly used image files. Whether you’re designing for media, creating visuals for business, or sharing memories online, understanding different file formats is essential. The JPG format is a type of raster image that uses compression to balance quality and file size, making it ideal for various applications. This guide will explain everything about JPG/JPEG files, from their history and technical details to practical uses, ensuring you have a complete understanding of this versatile image format.
Key takeaways
- JPG (or JPEG) is a popular image file format known for its efficient compression, making it ideal for digital photography and web graphics.
- The format was developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) and is universally recognized on various platforms.
- Both JPG and JPEG are the same format, with the difference in their extensions (.jpg and .jpeg) due to historical system limitations.
- JPG files use lossy compression, which balances file size and image quality but may cause quality loss with repeated editing.
- They are widely used for online images, social media, photo sharing, and document presentations.
- Tools like CoolUtils allow users to convert JPG to other formats such as PDF, PNG, and TIFF.
What are JPG and JPEG Files?
JPG and JPEG are two names for the same digital image format. Both refer to the format developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG), an international organization that standardized the JPEG format under ISO. The only difference between the two is the file extension: .jpg and .jpeg. This variation originated due to early operating systems like Windows, which limited file extensions to three letters, resulting in “.jpg”. Meanwhile, other systems like macOS and Linux had no such restriction, allowing “.jpeg”.
Both JPG and JPEG formats are known for their compression capabilities, making them ideal for storing and sharing digital images without taking up too much space. They are raster image formats, which means they use pixels to create images, making them perfect for detailed, colorful visuals but less suited for sharp-edged designs or logos. Despite compression, these formats can maintain good image quality, especially at higher resolutions, making them popular for web graphics, digital photography, and general media use.
Why do both JPG and JPEG exist?
What is JPG used for? JPG exists because early Windows operating systems limited file extensions to three letters. This led to “.jpg” instead of the full “.jpeg”. In contrast, UNIX-based systems (like macOS and Linux) had no such restriction, allowing “.jpeg” without issue. Over time, Windows updated to support longer extensions, but the “.jpg” format persisted for compatibility.
Today, both JPG and JPEG are universally recognized as the same digital image format. Most software and online platforms support both extensions, making them interchangeable. There is no difference in image quality, compression, or functionality between the two. This dual naming is simply a historical artifact of early operating systems.
How did JPEG files get their name?
JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group, the organization that developed this standardized format in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Recognized by ISO, it was created to efficiently store and compress digital images, especially for use with early digital cameras. Since then, JPEG has become the most popular format for images on the web and in digital photography.
History of the JPG Format
The JPG format was officially introduced in 1992 with the creation of the JPEG File Interchange Format (JFIF). Developed to replace bulky BMP files, this standard offered efficient compression algorithms for reducing file size without severe quality loss. It became the preferred format for digital cameras, enabling users to store more images without sacrificing clarity.
The JPEG standard balanced file size reduction and image quality, making it ideal for web graphics, email attachments, and digital photography. Its broad compatibility with software and devices further boosted its popularity. Over time, the format’s ability to efficiently compress digital photos without excessive quality loss made it a universal choice for both professional and casual users.
What is the Joint Photographic Experts Group?
The Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) is a technical industry group responsible for creating the JPEG image format, a global standard for digital images. It operates as a subcommittee of the ISO (International Organization for Standardization), an independent organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, with 167 national member bodies. Established to develop international standards for image compression, the group includes experts in technology, photography, and software development.
The JPEG format is officially defined under ISO/IEC 10918-1, making it a widely recognized standard. This format was developed to ensure consistent quality and compatibility for digital images across different software and devices. The group’s work has been essential in shaping the way digital images are stored, shared, and displayed worldwide.
How do JPEG Files Work?
JPEG files use lossy compression, a method that reduces file size by selectively removing image data. Images are divided into small squares (blocks), and each block is individually compressed. This technique allows for efficient storage and quick sharing but can result in slight quality loss.
JPEG images support 24-bit color, displaying up to 16.8 million colors, making them ideal for rich, colorful visuals. While this format is excellent for general use, repeated editing and saving can further reduce image quality due to the compression process.
Similarities and Characteristics of JPG and JPEG
JPG and JPEG are essentially identical, sharing the same core characteristics as raster image formats. Both use a grid of pixels to represent images, making them ideal for photos, artworks, and other visuals with subtle color transitions. This pixel-based structure allows them to display rich, detailed images, but it also means that enlarging them can result in visible quality loss, as each pixel becomes more noticeable.
These formats are known for their compression capabilities, which balance file size and image quality. By using lossy compression, JPG and JPEG reduce image data to save storage space. This process is efficient for sharing images online or storing them on devices without consuming too much memory. However, this compression also means that every time an image is saved, a small amount of quality is lost, especially after multiple edits.
Despite this, JPG and JPEG remain popular for various applications, from digital photography to web graphics and email attachments. They are particularly suitable for nonlined images, such as photos and subtly-hued graphics, but less effective for sharp-edged visuals like logos or text-based designs. Their wide compatibility with software, devices, and online platforms further adds to their popularity.
In summary, JPG and JPEG formats are versatile, widely used, and efficient for most digital image needs. They offer a balance between high-quality visuals and manageable file sizes, making them a standard choice for both professionals and everyday users.
What are JPG/JPEG Files Used For?
JPG/JPEG files are widely used for various digital imaging needs due to their efficient compression, making them perfect for web usage, digital photography, and social media. Their small file sizes ensure quick loading times, making them ideal for websites and online platforms.
For everyday users, JPGs are perfect for sharing images via email attachments, cloud storage, and social media posts. They are also commonly used in presentations and documents, providing a balance between image quality and file size.
Serious photographers may prefer raw formats for editing, as these preserve full image data without compression. However, JPGs remain a mainstream favorite for final delivery because of their compatibility with nearly all devices and software. Whether for quick sharing, online galleries, or professional presentations, JPG/JPEG files are versatile and practical.
Pros and Cons of JPEG Files
JPEG files offer a balanced trade-off between image quality and file size, making them a popular choice for digital images. They are universally recognized, compatible with most devices and software, and efficient for online sharing due to their small size. The lossy compression method reduces file size by removing less critical data, which speeds up loading times for web images and makes storage efficient.
However, this compression can lead to artifacts, such as posterization, where subtle color gradients appear as solid color blocks. Images with sharp edges, like logos or text, may become blocky or fuzzy, losing detail. Each time a JPEG image is edited and saved, the quality further degrades. These limitations make JPEG less suitable for precise graphics or images requiring high detail.
Despite these drawbacks, JPEGs remain ideal for photos, digital art with soft color transitions, and any situation where file size is a priority over perfect image quality. Their universal compatibility ensures they can be viewed and shared across almost all devices.
How to Open JPG Files on Different Devices
To open JPG files on a Windows PC, use File Explorer, right-click the file, and choose “Open with” to select the default image viewer (Photos). On macOS, use Preview by double-clicking the image, or right-click and choose “Open With”.
On Android, open the image using the default Gallery app. For iPhones, the Photos app opens JPG images automatically. To open JPGs on a web page, right-click (or Command-click) and choose “Open in a new tab”. Most devices automatically recognize and open JPG files, making them universally accessible.
Using Online Tools and Third-Party Applications
If you need to edit or convert JPG files, online tools like Canva are perfect for design tasks, while TinyPNG helps compress images without significant quality loss. These tools offer quick, user-friendly solutions without installing software.
For more advanced editing, use software like Adobe Photoshop. Online converters can also change JPG files into other formats (PNG, PDF), providing flexibility for various needs. Always choose tools that match your editing or conversion requirements.
How to Create and Edit JPEG Files
To create and edit JPEG files, software like Adobe Photoshop is a common choice. Open your image in Photoshop, then use the “File” menu, select “Save As”, and choose JPEG as the file format. Adjust the compression level to balance image quality and file size.
However, JPEG’s lossy compression means that each time you save the image, some quality is lost. For works-in-progress, save in a lossless format (like PSD) until you complete your edits. Only convert to JPEG when you are ready for the final version. This workflow prevents excessive quality degradation and ensures better image results.
JPEG Metadata and EXIF Data
JPEG files contain EXIF data (Exchangeable Image File Format), which stores information like camera settings, capture date, time, and even GPS location. To view this data on Windows, right-click the image, choose “Properties”, then go to “Details”. On macOS, open the image in Photos, click “Get Info”, and check the metadata details.
EXIF data is useful for photographers who want to track image settings or location information. However, be cautious when sharing images with location data for privacy reasons.
Converting JPG to Other Formats
JPG files can be converted to other formats depending on your needs. For documents, converting JPG to PDF is common, offering a more universal format. Online tools like CoolUtils JPG to PDF Converter let you resize to A4, A5, A3, or US letter, and even protect PDFs with a password. Speaking of JPEG, PDF vs JPEG, they are also possible to convert between each other.
You can also convert JPG to PNG, JPG to TIFF, and other formats. These conversions are useful for adjusting image quality, transparency (PNG), or maintaining maximum quality (TIFF). Select the format that best suits your project’s requirements.
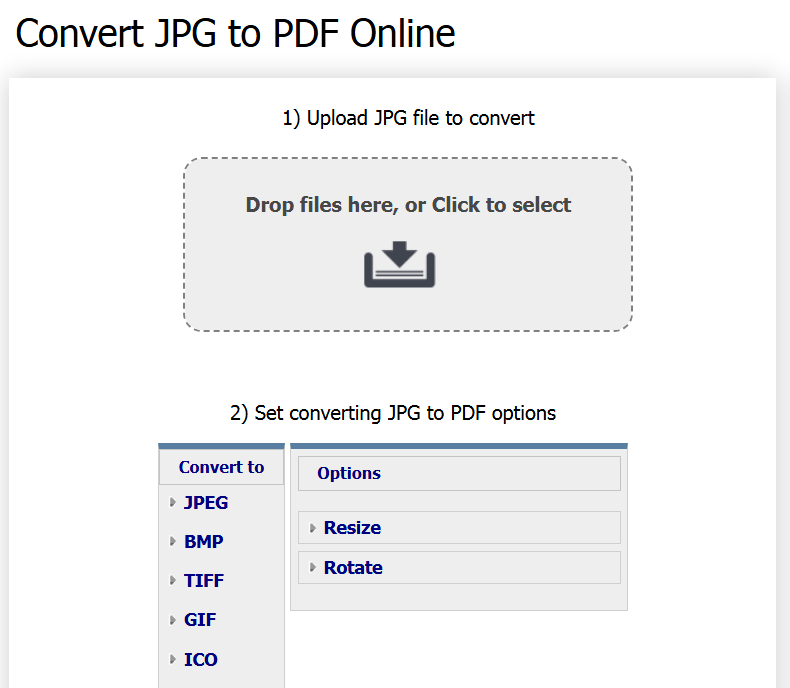
How to Convert JPG to Other Formats:
- Open CoolUtils JPG Converter.
- Select the JPG file you want to convert.
- Choose the desired output format (PDF, PNG, TIFF, SVG, EPS, MP4, HTML, DOCX, PSD, WEBP).
- Adjust settings as needed (resize, password protect, change resolution).
- Click “Convert” and download the converted file.
FAQs
How do I convert a photo to JPG?
Use an image editor like Adobe Photoshop, select “Save As”, and choose JPEG as the format. Online tools like CoolUtils JPG Converter also allow fast conversion without software installation.
What is the difference between PDF and JPG?
It is often asked about the difference between JPEG and PDF formats. PDF is a document format that can include text and images, while JPG is a compressed image format. PDF maintains layout and formatting, while JPG focuses on image storage and quality.
How to make a JPG file?
Open your image in an editor like Photoshop, click “Save As”, and select JPEG. Adjust the quality settings as needed. Online tools also offer direct conversion to JPG.
Is JPG the same as a photo?
No. There is sometimes a misunderstanding around what is JPG file extension. JPG is an image file format used for storing digital photos. A photo can exist in various formats, including JPG, PNG, TIFF, or RAW.
How do I convert a document to JPG?
Upload the document to an online converter like CoolUtils, choose “Convert to JPG”, and download the converted file. Alternatively, take a screenshot of the document and save it as a JPG.